Due to Greece's long periods of sunshine, skin health is an immediate priority, especially as there is an increase in melanoma cases and mortality.
More specifically, melanoma accounted for 4% of all new cancer diagnoses in the EU-27 countries in 2020 and 1.3% of all cancer deaths, according to the European Cancer Information System, and is the sixth most common cancer for both men and women.
In fact, 2022 sees a greater upward trend, with over 100,000 new cases of melanoma reported – most of them in adults aged 45-69 – causing more than 15,000 deaths.
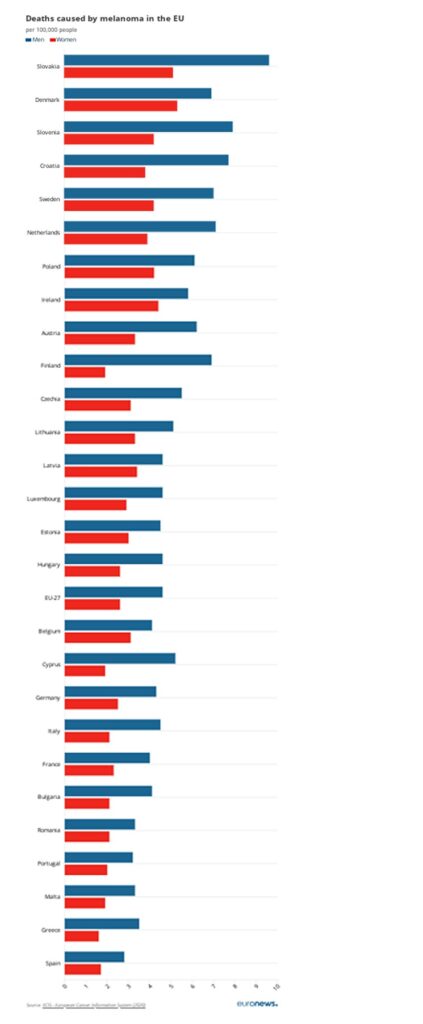
Even more worryingly, Greece is among the countries with the highest melanoma mortality - both for men and women, along with Spain, Portugal, Malta and Romania.
In contrast, the countries with the lowest mortality are Slovakia, Denmark, Slovenia, Croatia, Sweden and the Netherlands.
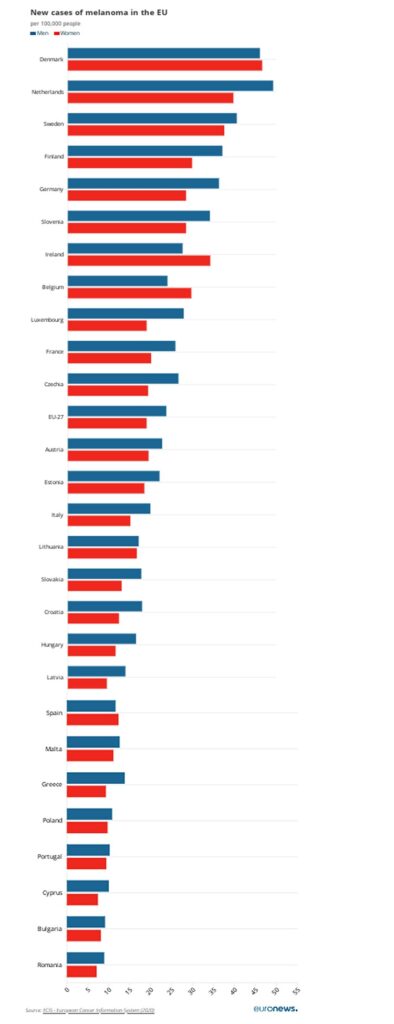
Despite this, Greece is not among the countries with the highest incidence rates of melanoma. These countries include Denmark, the Netherlands, Sweden, Finland and Germany.
Countries with the lowest rates include Romania, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Portugal and Poland.
Regarding the use of sunscreen, only 10% of Europeans regularly or frequently use sunscreen, along with other protective measures such as a hat, staying in the shade, compared to 14% of people outside Europe.
"Anyone can get skin cancer, regardless of age, gender, or skin tone. In fact, it is estimated that one in five Americans will develop skin cancer in their lifetime. Regular daily use of SPF 15 sunscreen can reduce your risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) by about 40 per cent and lower your melanoma risk by 50 per cent," advises the Skin Cancer Foundation on its website.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is the second most common form of skin cancer, characterised by abnormal, accelerated growth of squamous cells – a type of epithelial cells that make up the outer layer of the skin (in the epidermis).
If caught early, most SCCs are curable.
Melanoma is an aggressive form of skin cancer that begins when cells known as melanocytes (the cells that give the skin its tanned or brown color) begin to grow out of control.
While melanoma occurs less frequently, it is more dangerous because of its ability to spread quickly to other organs if not treated at an early stage.
READ MORE: Why Fakes and Fasolada are Considered Superfoods of the World.

